|
|
--- |
|
|
language: |
|
|
- en |
|
|
license: cc-by-nc-4.0 |
|
|
size_categories: |
|
|
- 1K<n<10K |
|
|
task_categories: |
|
|
- image-text-to-text |
|
|
- visual-question-answering |
|
|
- multiple-choice |
|
|
tags: |
|
|
- vision-language |
|
|
- multimodal |
|
|
- benchmark |
|
|
- chess |
|
|
- chemistry |
|
|
- music |
|
|
- graph-theory |
|
|
- semantic-equivalence |
|
|
- VLM |
|
|
dataset_info: |
|
|
features: |
|
|
- name: task |
|
|
dtype: string |
|
|
- name: domain |
|
|
dtype: string |
|
|
- name: index |
|
|
dtype: int32 |
|
|
- name: question_type |
|
|
dtype: string |
|
|
- name: question |
|
|
dtype: string |
|
|
- name: notation |
|
|
dtype: string |
|
|
- name: notation_type |
|
|
dtype: string |
|
|
- name: option_a |
|
|
dtype: string |
|
|
- name: option_b |
|
|
dtype: string |
|
|
- name: option_c |
|
|
dtype: string |
|
|
- name: option_d |
|
|
dtype: string |
|
|
- name: correct_answer |
|
|
dtype: string |
|
|
- name: correct_idx |
|
|
dtype: int32 |
|
|
- name: image |
|
|
dtype: image |
|
|
splits: |
|
|
- name: fork |
|
|
num_bytes: 0 |
|
|
num_examples: 200 |
|
|
- name: legal |
|
|
num_bytes: 0 |
|
|
num_examples: 200 |
|
|
- name: puzzle |
|
|
num_bytes: 0 |
|
|
num_examples: 200 |
|
|
- name: eval |
|
|
num_bytes: 0 |
|
|
num_examples: 200 |
|
|
- name: carbon |
|
|
num_bytes: 0 |
|
|
num_examples: 200 |
|
|
- name: hydrogen |
|
|
num_bytes: 0 |
|
|
num_examples: 200 |
|
|
- name: weight |
|
|
num_bytes: 0 |
|
|
num_examples: 200 |
|
|
- name: caption |
|
|
num_bytes: 0 |
|
|
num_examples: 200 |
|
|
- name: notes |
|
|
num_bytes: 0 |
|
|
num_examples: 200 |
|
|
- name: measures |
|
|
num_bytes: 0 |
|
|
num_examples: 200 |
|
|
- name: forms |
|
|
num_bytes: 0 |
|
|
num_examples: 200 |
|
|
- name: rhythm |
|
|
num_bytes: 0 |
|
|
num_examples: 200 |
|
|
- name: path_counting |
|
|
num_bytes: 0 |
|
|
num_examples: 200 |
|
|
- name: path_existence |
|
|
num_bytes: 0 |
|
|
num_examples: 200 |
|
|
- name: shortest_path |
|
|
num_bytes: 0 |
|
|
num_examples: 200 |
|
|
- name: bfs_traversal |
|
|
num_bytes: 0 |
|
|
num_examples: 200 |
|
|
download_size: 0 |
|
|
dataset_size: 0 |
|
|
configs: |
|
|
- config_name: default |
|
|
data_files: |
|
|
- split: fork |
|
|
path: data/fork-* |
|
|
- split: legal |
|
|
path: data/legal-* |
|
|
- split: puzzle |
|
|
path: data/puzzle-* |
|
|
- split: eval |
|
|
path: data/eval-* |
|
|
- split: carbon |
|
|
path: data/carbon-* |
|
|
- split: hydrogen |
|
|
path: data/hydrogen-* |
|
|
- split: weight |
|
|
path: data/weight-* |
|
|
- split: caption |
|
|
path: data/caption-* |
|
|
- split: notes |
|
|
path: data/notes-* |
|
|
- split: measures |
|
|
path: data/measures-* |
|
|
- split: forms |
|
|
path: data/forms-* |
|
|
- split: rhythm |
|
|
path: data/rhythm-* |
|
|
- split: path_counting |
|
|
path: data/path_counting-* |
|
|
- split: path_existence |
|
|
path: data/path_existence-* |
|
|
- split: shortest_path |
|
|
path: data/shortest_path-* |
|
|
- split: bfs_traversal |
|
|
path: data/bfs_traversal-* |
|
|
--- |
|
|
|
|
|
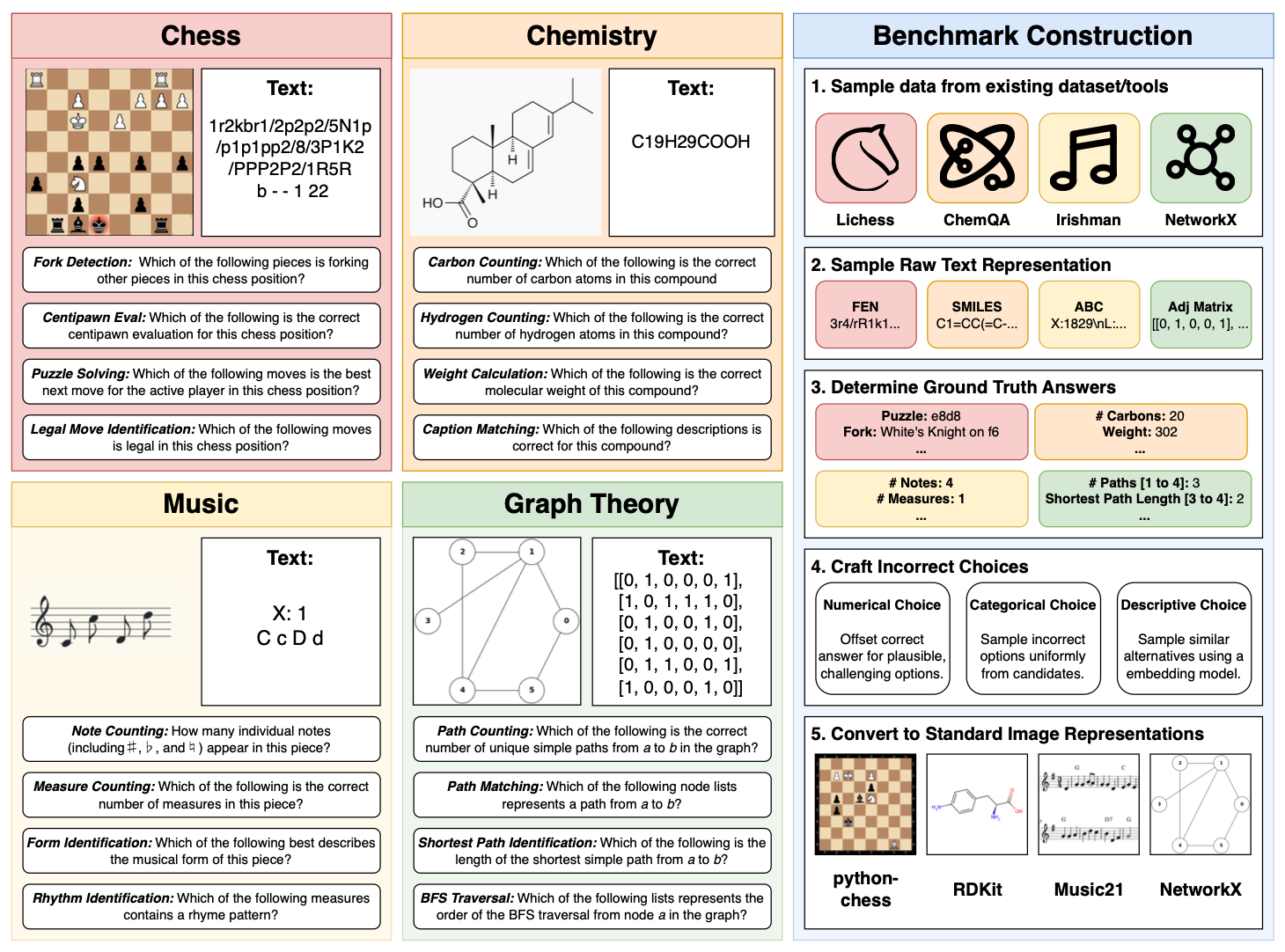
# SEAM: Semantically Equivalent Across Modalities Benchmark for Vision-Language Models |
|
|
|
|
|
*[CSSLab](https://csslab.cs.toronto.edu/), Department of Computer Science, University of Toronto* |
|
|
*[COLM '25] Second Conference on Language Modeling* |
|
|
|
|
|
- **Paper**: [Paper](https://huggingface.co/papers/2508.18179) |
|
|
- **Project Page / Leaderboard**: [SEAM Benchmark](https://lilv98.github.io/SEAM-Website/) |
|
|
- **Code**: [GitHub](https://github.com/CSSLab/SEAM) |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
## Abstract |
|
|
|
|
|
Evaluating whether vision-language models (VLMs) reason consistently across representations is challenging because modality comparisons are typically confounded by task differences and asymmetric information. We introduce SEAM, a benchmark that pairs semantically equivalent inputs across four domains that have existing standardized textual and visual notations. By employing distinct notation systems across modalities, in contrast to OCR-based image-text pairing, SEAM provides a rigorous comparative assessment of the textual-symbolic and visual-spatial reasoning capabilities of VLMs. Across 21 contemporary models, we observe systematic modality imbalance: vision frequently lags language in overall performance, despite the problems containing semantically equivalent information, and cross-modal agreement is relatively low. Our error analysis reveals two main drivers: textual perception failures from tokenization in domain notation and visual perception failures that induce hallucinations. We also show that our results are largely robust to visual transformations. SEAM establishes a controlled, semantically equivalent setting for measuring and improving modality-agnostic reasoning. |
|
|
|
|
|
## Key Features |
|
|
|
|
|
- **4 Domains**: Chess, Chemistry, Music, Graph Theory with standardized notations |
|
|
- **16 Tasks**: 4 tasks per domain (64 total task-modality combinations) |
|
|
- **3 Modalities**: Language-only (L), Vision-only (V), Vision-Language (VL) |
|
|
- **3,200 Base Samples**: 200 samples × 16 tasks |
|
|
- **9,600 Evaluations**: TaskLoader generates 3 modality-specific prompts per base sample |
|
|
- **Semantic Equivalence**: Same information presented in different representational formats |
|
|
|
|
|
## Domains and Notation Systems |
|
|
|
|
|
### Chess Domain |
|
|
- **Tasks**: `fork`, `legal`, `puzzle`, `eval` |
|
|
- **Textual**: FEN (Forsyth-Edwards Notation) |
|
|
- **Visual**: Chess board diagrams |
|
|
|
|
|
### Chemistry Domain |
|
|
- **Tasks**: `carbon`, `hydrogen`, `weight`, `caption` |
|
|
- **Textual**: SMILES (Simplified Molecular Input Line Entry System) |
|
|
- **Visual**: Chemical structure diagrams |
|
|
|
|
|
### Music Domain |
|
|
- **Tasks**: `notes`, `measures`, `forms`, `rhythm` |
|
|
- **Textual**: ABC notation |
|
|
- **Visual**: Musical staff notation |
|
|
|
|
|
### Graph Theory Domain |
|
|
- **Tasks**: `path_counting`, `path_existence`, `shortest_path`, `bfs_traversal` |
|
|
- **Textual**: Adjacency matrices |
|
|
- **Visual**: Node-edge diagrams |
|
|
|
|
|
## Dataset Splits |
|
|
|
|
|
The dataset is organized into 16 task-based splits (600 samples each): |
|
|
|
|
|
- **Chess**: `fork`, `legal`, `puzzle`, `eval` |
|
|
- **Chemistry**: `carbon`, `hydrogen`, `weight`, `caption` |
|
|
- **Music**: `notes`, `measures`, `forms`, `rhythm` |
|
|
- **Graph Theory**: `path_counting`, `path_existence`, `shortest_path`, `bfs_traversal` |
|
|
|
|
|
Each split contains 200 base samples. TaskLoader generates modality-specific prompts (L, V, VL) from these base samples. |
|
|
|
|
|
## Usage |
|
|
|
|
|
```python |
|
|
from datasets import load_dataset |
|
|
|
|
|
# Load the dataset |
|
|
dataset = load_dataset("lilvjosephtang/SEAM-Benchmark") |
|
|
|
|
|
# Access specific tasks |
|
|
chess_fork = dataset["fork"] # Chess fork detection (600 samples) |
|
|
chemistry_carbon = dataset["carbon"] # Carbon atom counting (600 samples) |
|
|
|
|
|
# Each task contains 200 base samples |
|
|
# TaskLoader generates modality-specific prompts (L/V/VL) from these base samples |
|
|
print(f"Task {chess_fork[0]['task']} has {len(chess_fork)} base samples") |
|
|
|
|
|
# Example sample structure |
|
|
sample = chess_fork[0] |
|
|
print(f"Task: {sample['task']}") |
|
|
print(f"Domain: {sample['domain']}") |
|
|
# No modality field - TaskLoader handles modality generation |
|
|
print(f"Question: {sample['question']}") |
|
|
print(f"Options: A) {sample['option_a']}, B) {sample['option_b']}, C) {sample['option_c']}, D) {sample['option_d']}") |
|
|
print(f"Correct Answer: {sample['correct_answer']}") |
|
|
print(f"Notation: {sample['notation']}") # FEN string for chess |
|
|
# sample['image'] contains the chess board image for Vision/Vision-Language modalities |
|
|
``` |
|
|
|
|
|
## Sample Structure |
|
|
|
|
|
Each sample contains: |
|
|
- `task`: Task identifier (e.g., "fork", "carbon") |
|
|
- `domain`: Domain category ("chess", "chemistry", "music", "graph") |
|
|
- No modality field (TaskLoader generates modality-specific prompts) |
|
|
- `index`: Sample index within the task |
|
|
- `question`: Question text (if applicable) |
|
|
- `notation`: Domain-specific notation (FEN, SMILES, ABC, adjacency matrix) |
|
|
- `notation_type`: Type of notation used |
|
|
- `option_a`, `option_b`, `option_c`, `option_d`: Multiple choice options |
|
|
- `correct_answer`: The correct answer |
|
|
- `correct_idx`: Index of the correct option |
|
|
- `image`: Associated image (PIL Image, None for base storage - TaskLoader handles image loading for V/VL modalities) |
|
|
|
|
|
## Evaluation Protocol |
|
|
|
|
|
SEAM enables three types of evaluation: |
|
|
|
|
|
1. **Language**: Models receive only textual notation |
|
|
2. **Vision**: Models receive only visual representation |
|
|
3. **Vision-Language**: Models receive both notation and image |
|
|
|
|
|
The semantic equivalence across modalities allows for direct comparison of reasoning capabilities and cross-modal agreement analysis. |
|
|
|
|
|
## Citation |
|
|
|
|
|
```bibtex |
|
|
@inproceedings{ |
|
|
tang2025seam, |
|
|
title={{SEAM}: Semantically Equivalent Across Modalities Benchmark for Vision-Language Models}, |
|
|
author={Zhenwei Tang and Difan Jiao and Blair Yang and Ashton Anderson}, |
|
|
booktitle={Second Conference on Language Modeling}, |
|
|
year={2025}, |
|
|
url={https://openreview.net/forum?id=lI4LgGv4sX} |
|
|
} |
|
|
@misc{tang2025seamsemanticallyequivalentmodalities, |
|
|
title={SEAM: Semantically Equivalent Across Modalities Benchmark for Vision-Language Models}, |
|
|
author={Zhenwei Tang and Difan Jiao and Blair Yang and Ashton Anderson}, |
|
|
year={2025}, |
|
|
eprint={2508.18179}, |
|
|
archivePrefix={arXiv}, |
|
|
primaryClass={cs.AI}, |
|
|
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2508.18179}, |
|
|
} |
|
|
``` |