Update dataset card: License, task category, paper link, and abstract (#2)
Browse files- Update dataset card: License, task category, paper link, and abstract (ecb6e3286c41afae5da4df69f7ef998924022f6b)
Co-authored-by: Niels Rogge <[email protected]>
README.md
CHANGED
|
@@ -1,10 +1,13 @@
|
|
| 1 |
---
|
| 2 |
-
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 3 |
task_categories:
|
|
|
|
| 4 |
- visual-question-answering
|
| 5 |
- multiple-choice
|
| 6 |
-
language:
|
| 7 |
-
- en
|
| 8 |
tags:
|
| 9 |
- vision-language
|
| 10 |
- multimodal
|
|
@@ -15,8 +18,6 @@ tags:
|
|
| 15 |
- graph-theory
|
| 16 |
- semantic-equivalence
|
| 17 |
- VLM
|
| 18 |
-
size_categories:
|
| 19 |
-
- 1K<n<10K
|
| 20 |
dataset_info:
|
| 21 |
features:
|
| 22 |
- name: task
|
|
@@ -140,15 +141,15 @@ configs:
|
|
| 140 |
*[CSSLab](https://csslab.cs.toronto.edu/), Department of Computer Science, University of Toronto*
|
| 141 |
*[COLM '25] Second Conference on Language Modeling*
|
| 142 |
|
| 143 |
-
- **Paper**: [
|
| 144 |
-
- **Leaderboard**: [SEAM Benchmark](https://lilv98.github.io/SEAM-Website/)
|
| 145 |
- **Code**: [GitHub](https://github.com/CSSLab/SEAM)
|
| 146 |
|
| 147 |
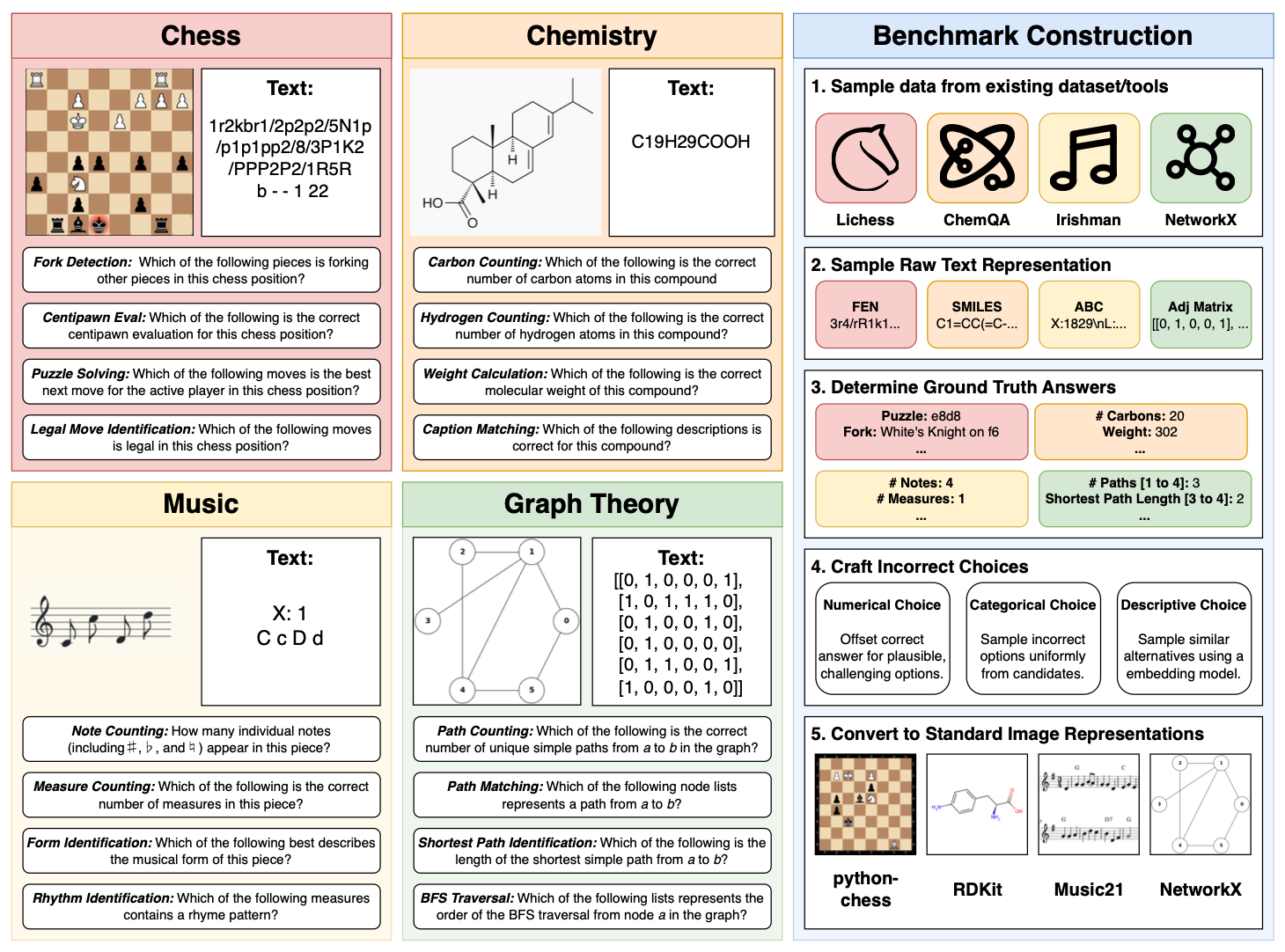
|
| 148 |
|
| 149 |
## Abstract
|
| 150 |
|
| 151 |
-
Evaluating whether vision
|
| 152 |
|
| 153 |
## Key Features
|
| 154 |
|
|
@@ -239,13 +240,12 @@ Each sample contains:
|
|
| 239 |
|
| 240 |
SEAM enables three types of evaluation:
|
| 241 |
|
| 242 |
-
1.
|
| 243 |
-
2.
|
| 244 |
-
3.
|
| 245 |
|
| 246 |
The semantic equivalence across modalities allows for direct comparison of reasoning capabilities and cross-modal agreement analysis.
|
| 247 |
|
| 248 |
-
|
| 249 |
## Citation
|
| 250 |
|
| 251 |
```bibtex
|
|
@@ -266,5 +266,4 @@ The semantic equivalence across modalities allows for direct comparison of reaso
|
|
| 266 |
primaryClass={cs.AI},
|
| 267 |
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2508.18179},
|
| 268 |
}
|
| 269 |
-
```
|
| 270 |
-
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
---
|
| 2 |
+
language:
|
| 3 |
+
- en
|
| 4 |
+
license: cc-by-nc-4.0
|
| 5 |
+
size_categories:
|
| 6 |
+
- 1K<n<10K
|
| 7 |
task_categories:
|
| 8 |
+
- image-text-to-text
|
| 9 |
- visual-question-answering
|
| 10 |
- multiple-choice
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 11 |
tags:
|
| 12 |
- vision-language
|
| 13 |
- multimodal
|
|
|
|
| 18 |
- graph-theory
|
| 19 |
- semantic-equivalence
|
| 20 |
- VLM
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 21 |
dataset_info:
|
| 22 |
features:
|
| 23 |
- name: task
|
|
|
|
| 141 |
*[CSSLab](https://csslab.cs.toronto.edu/), Department of Computer Science, University of Toronto*
|
| 142 |
*[COLM '25] Second Conference on Language Modeling*
|
| 143 |
|
| 144 |
+
- **Paper**: [Paper](https://huggingface.co/papers/2508.18179)
|
| 145 |
+
- **Project Page / Leaderboard**: [SEAM Benchmark](https://lilv98.github.io/SEAM-Website/)
|
| 146 |
- **Code**: [GitHub](https://github.com/CSSLab/SEAM)
|
| 147 |
|
| 148 |

|
| 149 |
|
| 150 |
## Abstract
|
| 151 |
|
| 152 |
+
Evaluating whether vision-language models (VLMs) reason consistently across representations is challenging because modality comparisons are typically confounded by task differences and asymmetric information. We introduce SEAM, a benchmark that pairs semantically equivalent inputs across four domains that have existing standardized textual and visual notations. By employing distinct notation systems across modalities, in contrast to OCR-based image-text pairing, SEAM provides a rigorous comparative assessment of the textual-symbolic and visual-spatial reasoning capabilities of VLMs. Across 21 contemporary models, we observe systematic modality imbalance: vision frequently lags language in overall performance, despite the problems containing semantically equivalent information, and cross-modal agreement is relatively low. Our error analysis reveals two main drivers: textual perception failures from tokenization in domain notation and visual perception failures that induce hallucinations. We also show that our results are largely robust to visual transformations. SEAM establishes a controlled, semantically equivalent setting for measuring and improving modality-agnostic reasoning.
|
| 153 |
|
| 154 |
## Key Features
|
| 155 |
|
|
|
|
| 240 |
|
| 241 |
SEAM enables three types of evaluation:
|
| 242 |
|
| 243 |
+
1. **Language**: Models receive only textual notation
|
| 244 |
+
2. **Vision**: Models receive only visual representation
|
| 245 |
+
3. **Vision-Language**: Models receive both notation and image
|
| 246 |
|
| 247 |
The semantic equivalence across modalities allows for direct comparison of reasoning capabilities and cross-modal agreement analysis.
|
| 248 |
|
|
|
|
| 249 |
## Citation
|
| 250 |
|
| 251 |
```bibtex
|
|
|
|
| 266 |
primaryClass={cs.AI},
|
| 267 |
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2508.18179},
|
| 268 |
}
|
| 269 |
+
```
|
|
|